
Manufacturers, power utilities and other industrial companies stand to gain the most in digital transformation. Industry accounts for 37% of total energy used globally, for instance, more than any other sector. By fine tuning operations with AI, some manufacturers can reduce carbon emission by up to 20% and save millions of dollars in the process.
Industry, however, remains relatively un-digitized and air gaps often exist between operational technology-the robots, furnaces and other equipment on factory floors—and the servers and storage systems that make up a company’s IT footprint. Of the 232.6 million pieces of fixed industrial equipment installed in 2020, only 10% were IIoT-enabled.
Why the gap? The technology hasn’t been good enough. Plants operate on exacting specifications. Engineers and plant managers need a “live” picture of operations with continual updates on temperature, pressure, power consumption and other variables from hundreds, if not thousands, of devices. Dropped, corrupted or mis-transmitted data can lead to unanticipated downtime—a $50 billion year problem—as well as injuries, blackouts, and even explosions.
Getting around these problems has required specialized technologies based around proprietary standards and complex component sets. As a result, many companies still monitor their most valuable assets the old-fashioned way: with an employee and a clipboard.
Enter the latest acronym: TSN or time sensitive networking. Based on the IEEE 802.1AS-2020 standards for Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) combines the performance requirements of industry with economies of scale and pace of innovation of standards-based Ethernet technology.
Done right, TSN will lower the capex and opex for industrial technology, open the door to integrating Industry 4.0 practices and simplify the process for bringing new equipment to market.
The Evolution of Ethernet
Ethernet was built for practicality. While you want to receive all of your emails, it typically doesn’t matter if your network receives them out of order before rearranging them chronologically in your inbox. With the advent of VoIP, determinism—i.e. the need for packets to be sent and received in a precise, synchronized fashion—suddenly became important. Phone calls wouldn’t make sense if your words (or the words you want to hear) got delivered out-of-order.
Industrial determinism is exponentially more challenging because the scale and speed of the data. Large oil companies need to track over 7.5 million data streams and perform 100,000 new calculations on that data every minute. Vibration analysis tools parse thousands of signals a second. Even less-demanding applications, such as beer brewing where data might get updated every few minutes, need precise synchronization to understand how a small change at the front of a process (a temperature spike) is causing problems (a build-up of acetyl) far down the line.
The TSN Standards in Action
For many equipment makers, the 802.1AS-2020 will be relatively new. Here is some idea of what you can expect:
IEEE 802.1AS-2020 – Timing and Synchronization for Time-Sensitive Applications
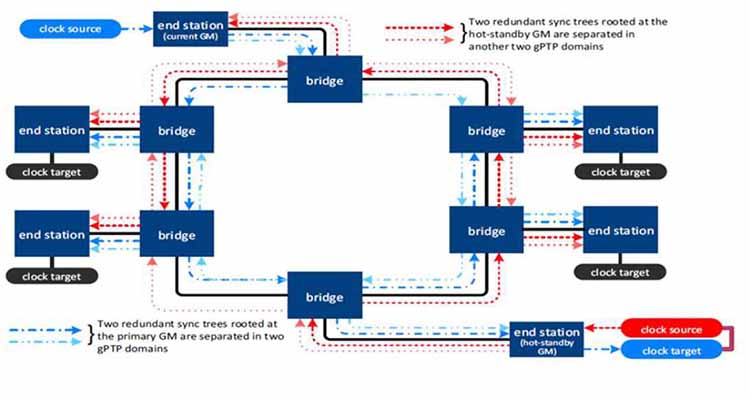
All switches end point and gateways devices on the TSN network must be time synchronized. In addition to the general IEEE 1588 specification, the TSN Task Group adopted a special standard 802.1AS-2020 for TSN synchronization.
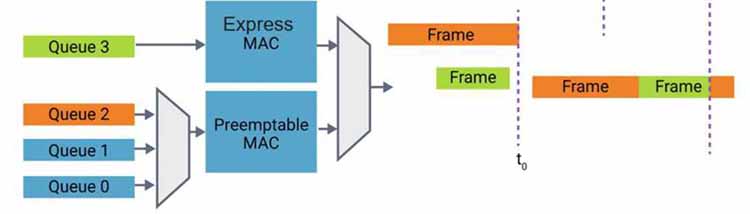
802.1Qbu / 802.3br frame preemption
In highly converged networks, higher priority traffic can be delayed by low priority frames. Frame preemption allows for reduction of transmission latency for express traffic, by preempting low priority packets. Frame preemption allows lowest deterministic latency for critical latency sensitive applications.
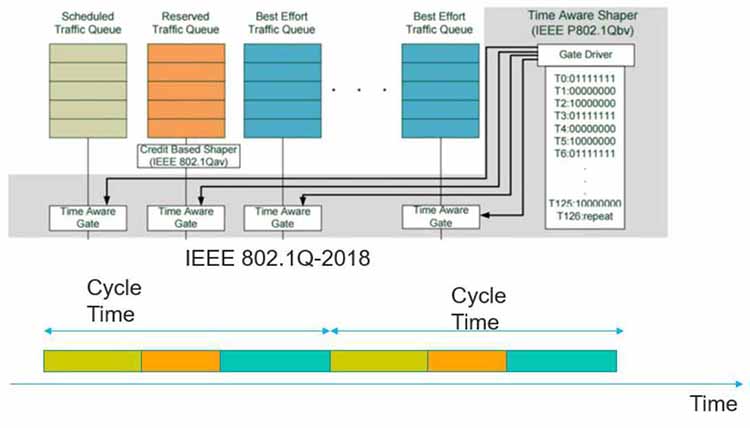
IEEE 802.1Qbv – TIME-AWARE SCHEDULER
The time-aware shaper is designed to separate the communication into fixed length, repeating time cycles. By doing this, it’s possible to grant exclusive use to the Ethernet transmission for those applications that need transmission guarantees and can’t be interrupted. Time aware shaper also allows guaranteed BW for these applications.
The IT Advantage
Bridging this divide will take work. Traditional IT vendors will have to better understand the concerns and cultures of OT departments. OT engineers can often give you a litany of IT technologies that failed to live up to expectations.
Still, the benefits of adoption will become apparent quickly. TSN-based products will deliver greater speeds and bandwidth than in the past. The wider range of solutions that happens with standards will increase choice and improve the TCO. And once the base network is installed, more applications will be added. Imagine a utility offering premium payments to an aluminum smelter or paper mill selling power for shifting some processes to non-peak hours on demand: applications like this are already delivering millions in revenue to some customers.
Do I expect OT and IT departments to join hands and sing on a mountaintop tomorrow? No, but the two sides are moving closer and TSN will play a critical part in closing the gap.













