Rapid advancements in compute intensive applications have raised the bar for a faster, more efficient, and scalable network. Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) over converged ethernet (RoCE) has emerged as a ground breaking technology that enables direct data transfer between systems without the intervention of CPU, reducing latency and enhancing overall system performance. iWave, an FPGA design house has taken a step further implementing 100G Ethernet solution by integrating ERNIC IP (Ethernet RDMA Network Interface Controller Intellectual Property) from AMD, bringing RDMA capabilities to their embedded computing modules portfolio.
What is RDMA over converged ethernet (RoCE)?
RDMA is a technology that allows direct memory transfers between hosts or servers without CPU involvement. This frees up CPUs for tasks like running applications and handling data processing, leading to enhanced network performance with reduced latency, CPU load, and increased bandwidth cost-effectively. While RoCE is a network protocol which allows RDMA over ethernet network. RoCE leverages the capabilities of RDMA while utilizing the standard Ethernet infrastructure, making it an attractive choice for organizations seeking performance improvements without overtaking their existing network setups.
Types of RoCE
There are two versions of RDMA over Converged Ethernet: RoCE v1 and RoCE v2, depending on the network adapter used.
- RoCE v1: This protocol allows communication between two hosts within the same Ethernet broadcast domain (VLAN). It utilizes Ethertype 0x8915, limiting standard Ethernet frames to 1500 bytes and Ethernet jumbo frames to 9000 bytes.
- RoCE v2: Overcoming the limitation of RoCE v1 to a single broadcast domain, RoCE v2 introduces changes in packet encapsulation by including IP and UDP headers. This modification enables RoCE v2 to function across both L2 (Data Link Layer) and L3 (Network Layer) networks, allowing Layer 3 routing and scalability across multiple subnets. Referred to as Routable RoCE (RRoCE), RoCE v2 also introduces the capability of IP multicast.

RoCEv1 vs RoCEv2 Packet Format
ERNIC IP Enhancing RDMA Capabilities
ERNIC (Embedded RDMA enabled NIC) IP is a customizable Ethernet RDMA Network Interface Controller IP core designed to work seamlessly with AMD FPGAs, MPSoCs, and soft MAC IP implementations. It provides high throughput, low-latency, and a completely hardware offloaded reliable data transfer solution over standard Ethernet.
iWave, at the forefront of cutting-edge technology has showcased the remarkable capabilities of its platform by successfully implementing 100G Ethernet solution. This was realized by using iWave’s Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC powered development kit and integrating AMD’s ERNIC IP on the platform. The Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC development kit is well suited for prototyping and evaluating 100G Ethernet solutions using high speed QSFP-28 connector.
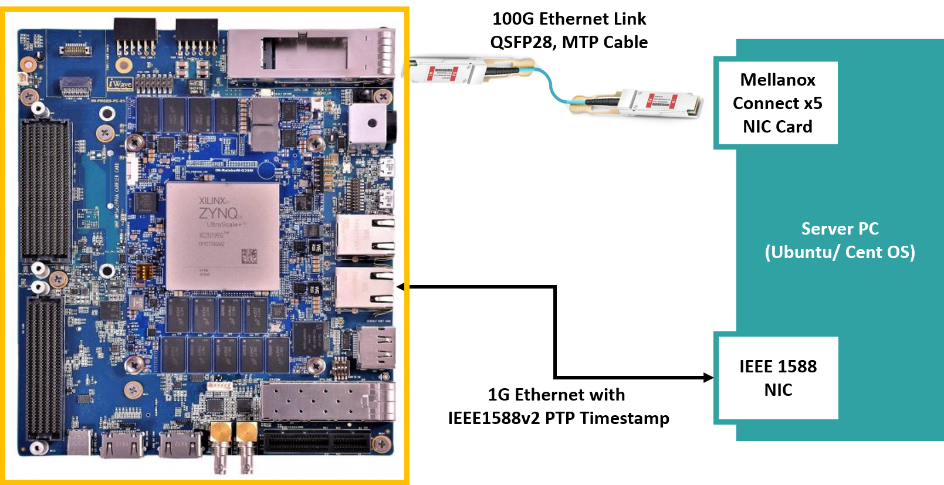
The demo setup included
- iWave’s Zynq Ultrascale+ MPSoC ZU19EG powered development kit
- Mellanox Connect x 5 100 G NIC
- Sync 1588 PTP Enabled 1G NIC
- MTP Cable, QSFP-28 Modules and CAT6 RJ45 Ethernet Cable
- Ubuntu 22.04 Server PC
System Architecture
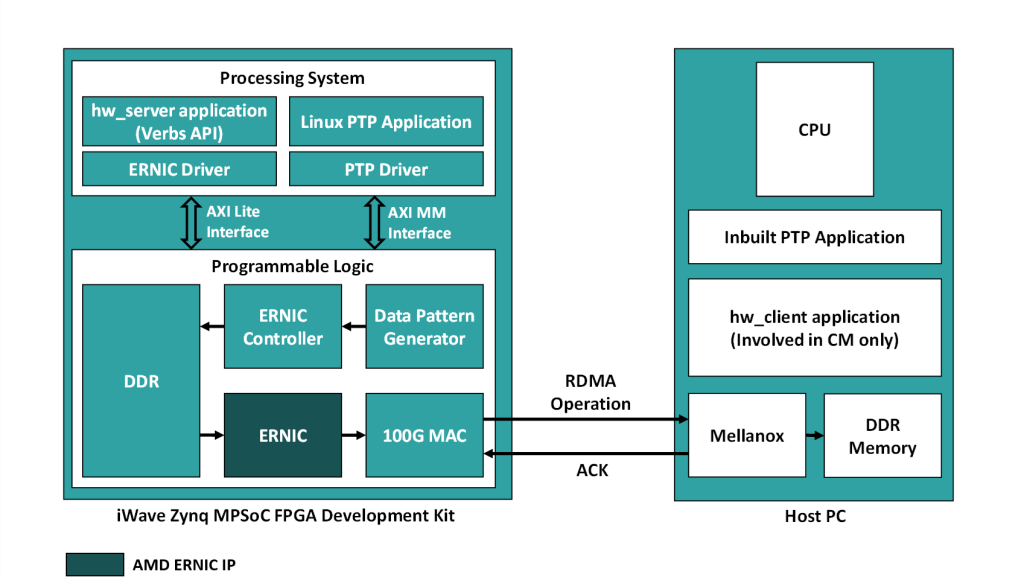
The high-level architecture is illustrated in the image above, with the implementation segmented between the Processing System (PS) and Programmable Logic (PL) components within the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC. The PS features an ARM Cortex-A53 based Hard SoC, which is used for essential system configuration, control, and diagnosis. This includes:
- 100G Ethernet MAC driver – Offering robust performance and low-latency support for data transmission at 100 Gb/s.
- ERNIC Controller driver – Responsible for posting incoming data to DDR and notifying ERNIC IP, this driver also efficiently manages doorbell exchanges between the user application and ERNIC IP.
- RDMA core and User Space Libraries – Ensures optimal performance and compatibility for RDMA operations in both kernel and user spaces.
The AMD ERNIC IP offloads the RoCEv2 Stack onto the FPGA. The ERNIC Controller manages handshaking with various modules to facilitate data transfer, generating work queue entries and ringing doorbells for the ERNIC IP. Meanwhile, the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC 100G Ethernet subsystem handles the MAC and Physical layers. Additionally, the Data Pattern Generator is tasked with generating both raw data and video data patterns.
PTP (IEEE 1588 Standard) timestamp is used to synchronize time between one system to another on an ethernet network. PTP timestamps enhance the performance of real-time applications by providing synchronized and low latency data exchange at nano second level.
Key highlights of the setup include:
- 100G Ethernet over RoCEv2 using AMD ERNIC IP
- Reliable Connection Transport Type
- RDMA SEND, RDMA READ, and RDMA WRITE for incoming and outgoing packets
- RDMA Send with Immediate, RDMA Write with Immediate Message Types
- RDMA Performance Test using XRPING and PERFTEST Applications
- Custom Data Pattern Generator with RAW and Video Data Pattern
- Insertion of PTP Timestamp along with Data
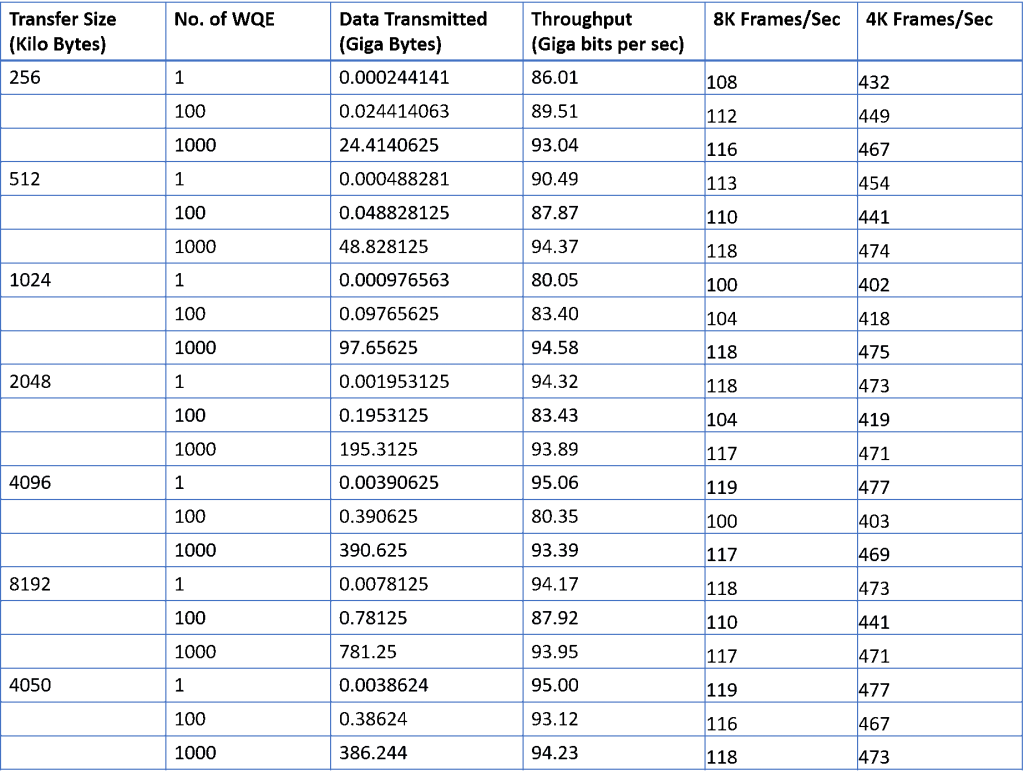
The detailed throughput statistics of the Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC development kit to server PC video data transfer is provided in Table below. The MPSoC development platform receives 8K video @ >100 fps and 4K video @ >400fps.

Potential Applications
RDMA over converged ethernet and ERNIC IP can unlock new opportunities and capabilities across multiple industries, enhancing connectivity, performance, and efficiency in diverse applications and environments. Few of such applications are listed here:
- Data Centers and Cloud Computing: Facilitate efficient communication between servers and accelerate data processing in cloud computing architectures.
- Video/Image Capture and Transfer: Beneficial for multimedia applications, broadcasting, and virtual reality (VR).
- Storage Solutions: Facilitate faster data transfers between storage devices and servers, contributing to improved storage system performance.
- High-Performance Computing (HPC): Enhance data transfer speeds and reduce latency in HPC clusters, facilitating faster computational tasks and simulations.
- IoT Edge Devices: Gather and transmit data from sensors and devices in real-time.
As the demand for faster and more efficient data transfer solutions continues to grow, RDMA over Converged Ethernet and ERNIC IP is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of high-performance computing.












