In many areas of telecommunications, information technology, network and data technology, it is recommended to use a specialized telecom power supply to achieve space, cost and energy saving, as well as high reliability. MORNSUN Telecom Power Supply VCB/VCF series features high power density, high efficiency, compact size and high reliability, which is designed to support reliable power supply systems for the communication industry.
However, some customers may encounter some questions when using VCB/VCF series, such as:
1) Why is the output voltage higher than expected? And how to handle it?
2) How to solve overheating problems when the operating temperature exceeds the derating temperature at full load?
3) What should be considered in PCB layout design?
This article provides suggested solutions to these common problems.
Q 1: Why is the output voltage higher than expected? And how to handle it?
Output voltage problems are usually due to incorrect connection of the function pins. MORNSUN Telecom Power Supply VCB/VCF series has two function pins that control the output voltage: the TRIM pin and the SENSE pin.

1.TRIM pin
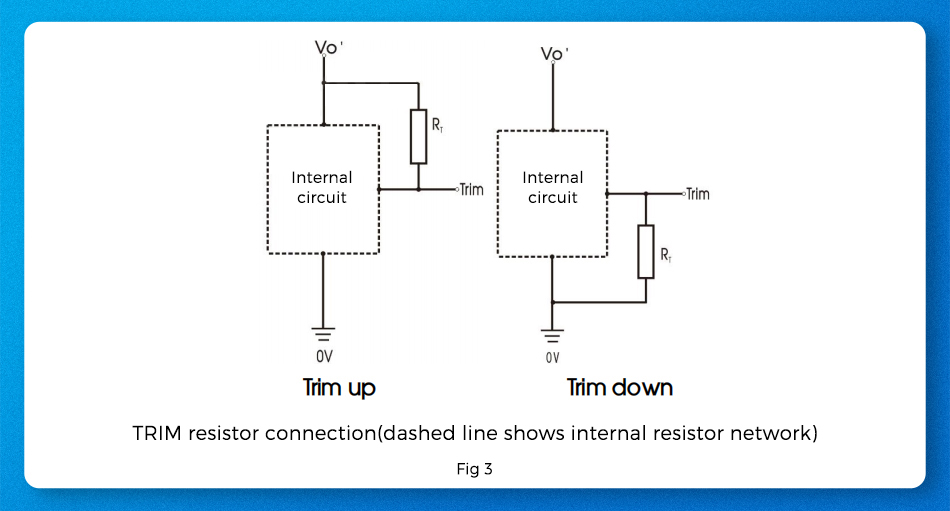
TRIM is the pin for output voltage adjustment, which is required to meet the telecom power supply positive logic of the DOSA: The TRIM pin is connected in series with a resistor to 0V to realize the voltage down, or in series with a resistor to Vo+ to realize the voltage up (Figure 3). If TRIM and Vo+ are short-circuited, the output voltage will be high. If voltage regulation is not required, leave them unconnected.
2.SENSE pin
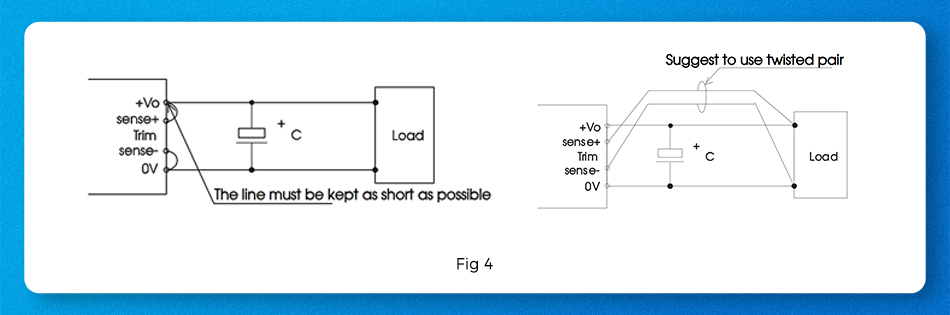
When remote compensation is not required, +SENSE should be connected directly to Vo+ and -SENSE should be connected directly to 0V, and the connecting wires should be as short as possible (Figure 4). If remote compensation is required to solve the problem of line loss caused by long load lines at the back end, +SENSE and -SENSE must be connected to the load at the back end.
Q 2: How to solve overheating problems when the operating temperature exceeds the derating temperature at full load?
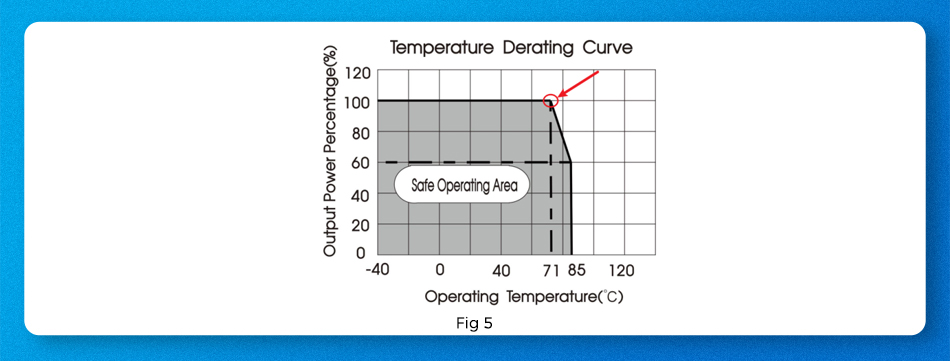
Open-frame brick package telecom power supplies usually need to solve the problem of “heat” during use. The telecom power supply itself has over temperature protection function, when the operating temperature exceeds the derating temperature of full load, how to solve the “heat” problem? Here are 2 methods:
1. Conductive heat dissipation
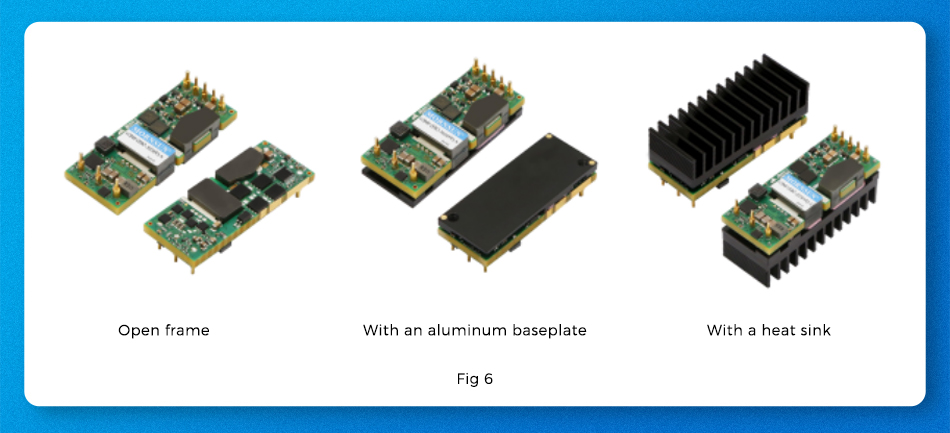
Telecom power supplies are generally available in three packages: open frame, with an aluminum baseplate, and with a heat sink. When the reference temperature derating curve cannot meet the application requirements in a non-ventilated environment, the heat dissipation operation can be referred to the external shell temperature point (as shown in Figure 7).
When selecting a power supply with an aluminum baseplate, apply heat-conducting glue to the heat sink or place a heat-conductive pad, bring the power supply in contact with the metal case of the application system, and use the metal case to dissipate heat from the power supply. This will reduce the hot spot temperature and increase the output power. Alternatively, simply choose a product with H-shaped heat sink.
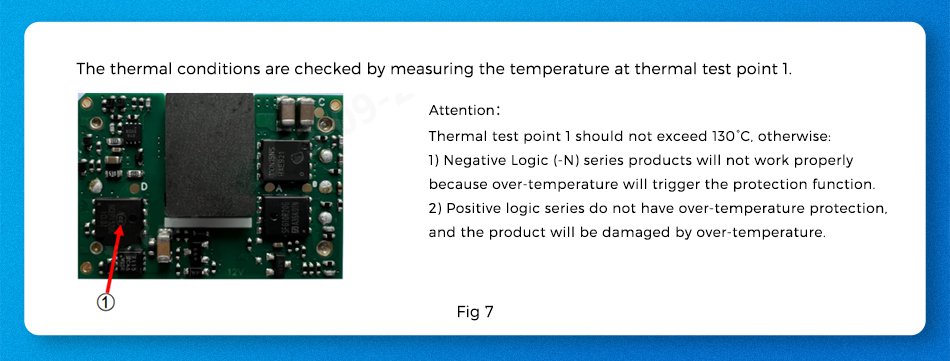
Note: When using in a closed system, it is important to consider the internal temperature of the system, rather than the external temperature, as the reference for environmental temperature.
2. Air-cooling
This is the more common method of heat dissipation, i.e. the higher the wind speed, the better the heat dissipation.
Q3: What should be considered in PCB layout design?
The layout design is critical, especially for EMC design and the effect of output voltage drop.
- To reduce the wire impedance, the wire between the SENSE pin and Vo+/0V should be as short as possible. If the remote compensation function is used, twisted pair or shielded wires should be used, and the wires should also be as short as possible.
- To keep the voltage drop between the power supply module and the load ≤ 0.3 and as low as possible, a wide copper PCB layout or wiring must be used.
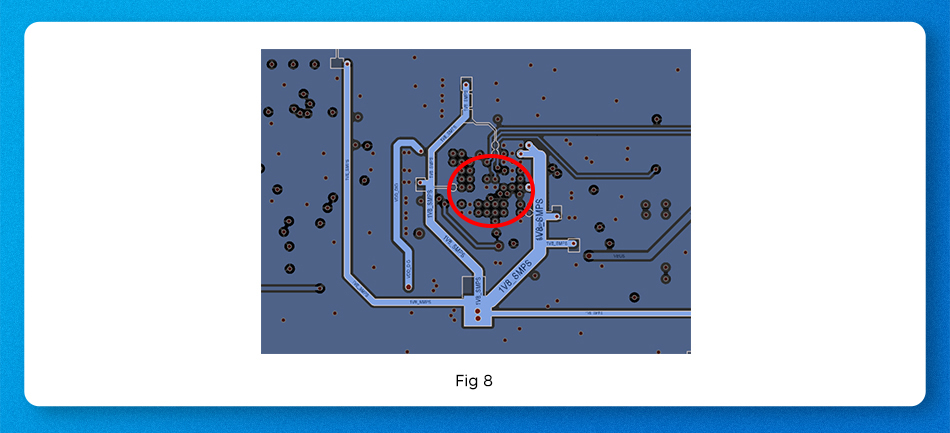
- To achieve good EMC performance, the copper PCB layout for the EMC circuit should be designed in according with the recommended circuit’s straight-line sequence, avoiding a “circular layout” (Figure 8). The circular layout is easy to introduce interference, fail to achieve the filtering effect of the power supply front end.
Summary
Any communication equipment needs a reliable power system to ensure smooth operation. MORNSUN Telecom power supply VCB/VCF series features an open frame brick package and cost-effective, high- power density, making it suitable for applications in the PoE, base stations, data centers, servers, and more. If you are puzzled by the problems you encounter when designing a power supply system, feel free to contact with MORNSUN’s FAEs or sales, and we are always ready to provide a variety of technologies and products to solve your problems.
Mornsun has always focused on the field of power supply design and manufacturing. From 3-1300W telecom DC/DC power supplies to EMC filters, we provide one-stop power supply solutions for the communications industry to simplify customers’ system design and ensure system safety and stability.
For more information, please visit www.mornsun-power.com












