Manufacturing/production, allied industries, and value-creation processes have undergone a digital transition known as “industry 4.0.”
Industry 4.0 refers to a new industrial revolution that will combine advanced manufacturing methods and the Internet of Things to create manufacturing systems that are not only interconnected but also communicate, analyze, and use information to motivate further intelligent action in the physical world.
As per Fortune Business Insights, the market for Industry 4.0 is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.4% from 2017 to 2028, reaching USD 337.10 billion. This growth would be aided by rising automated system adoption. According to projections, the market for industry 4.0 will increase from USD 64.9 billion in 2021 to USD 165.5 billion in 2026, growing at a CAGR of 20.6% throughout that time. The manufacturing sector’s quick adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), rising demand for industrial robots in the production of pharmaceuticals and medical devices, rising government investment in additive manufacturing and 3D printing, and expanding use of blockchain technology are the main factors driving the market’s growth.
How Industry 4.0 technologies are changing manufacturing
Industry 4.0 is transforming how businesses make, enhance, and distribute their goods. Manufacturers are incorporating new technology into their manufacturing facilities and processes, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), cloud computing and analytics, and AI and machine learning.
General Electric, Siemens, Honeywell, ABB, and Emerson Electric are some of the leading companies functioning in the industry market.
These smart factories are outfitted with cutting-edge sensors, embedded software, and robots that gather and analyze data to enable better decision making. When data from manufacturing operations is coupled with operational data from ERP, supply chain, customer service, and other business systems, new levels of visibility and insight are developed from previously isolated information.
Increased automation, preventative maintenance, self-optimization of process improvements, and, most importantly, a degree of efficiency and customer responsiveness previously unattainable were all made feasible by digital technology.
The manufacturing sector has a fantastic potential to join the fourth industrial revolution by developing smart factories. Real-time visibility of manufacturing assets is ensured by analyzing the massive volumes of big data gathered from sensors on the factory floor, which may also give tools for doing predictive maintenance to reduce equipment downtime.
Smart factories using IoT technology provide increased production and better quality. Manufacturing mistakes are decreased, and money and time are saved, when manual inspection business models are replaced with AI-powered visual insights. A smartphone connected to the cloud may be easily set up by quality control workers to enable remote monitoring of production operations. Manufacturers may identify mistakes earlier rather than later, when repair work is more expensive, by using machine learning algorithms.
All sorts of industrial businesses, including discrete and process manufacturing, as well as oil and gas, mining, and other industrial areas, may use Industry 4.0 concepts and technology.
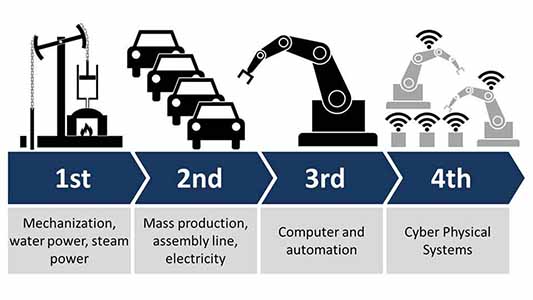
The Fourth Industrial Revolution, or Industry 4.0
A fourth industrial revolution, known as Industry 4.0, has evolved in the recent decades. With the aid of connection provided by the Internet of Things (IoT), access to real-time data, and the introduction of cyber-physical systems, Industry 4.0 elevates the current emphasis on digital technology to a completely new level. A more complete, connected, and all-encompassing approach to production is provided by Industry 4.0.

It links the physical and digital worlds and makes it easier for partners, vendors, partners, and individuals to collaborate and access information. As a result of Industry 4.0, business leaders are better able to manage and comprehend every part of their operations and may use real-time data to increase efficiency, streamline procedures, and spur development.
Basic IIoT Concepts and Glossary of Terms
Before deciding whether to invest in Industry 4.0 solutions for your company, you should be aware of the following 12 fundamental terms and ideas related to IIoT and Industry 4.0:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Tools for managing business processes that may be used to manage data across an organization.
- IoT: The term “Internet of Things” (IoT) refers to links between actual physical items, such as machinery or sensors, and the Internet.
- IIoT: The term “Industrial Internet of Things” (IIoT) refers to the connections between individuals, organizations, and machines as they pertain to production.
- Big data: Large collections of structured or unstructured data that may be collected, saved, arranged, and analyzed to find patterns, trends, relationships, and opportunities are referred to as “big data.”.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): Artificial intelligence is a term used to describe a computer’s capacity to carry out operations and reach choices that, in the past, would have required some degree of human intellect.
- M2M: Machine-to-machine communication, often known as M2M, takes place across wired or wireless networks between two different machines.
- Digitization: The act of gathering and transforming various forms of information into a digital format is known as digitization.
- Smart factory: Investments in Industry 4.0 technology, solutions, and methods are made by smart factories.
- Machine learning: The term “machine learning” describes how computers may use artificial intelligence to learn and develop on their own, without being expressly instructed or programmed to do so.
- Cloud computing: Information storage, management, and processing using networked distant servers that are hosted online is referred to as “cloud computing.”.
- Real-time data processing: The ability of computer systems and equipment to constantly and autonomously analyze data and give real-time or near-real-time outputs and insights is referred to as “real-time data processing.”.
- Ecosystem: Production ecosystems relate to the potential interconnections of your whole organization, including supply chain management, customer interactions, financial planning, inventories, and manufacturing execution.
- Cyber-physical systems (CPS): An industry 4.0-enabled manufacturing environment that delivers real-time data gathering, analysis, and transparency across every facet of a manufacturing process is referred to as cyber-physical systems, also known as cyber manufacturing.
Smart Manufacturing Use Cases
Consider how smart manufacturing may be used in your firm or a business that is comparable to yours in order to better comprehend the idea. Here are three examples of how Industry 4.0 might be used to improve manufacturing processes:
- Supply chain management and optimization—Businesses benefit from more knowledge, control, and data visibility across their whole supply chain thanks to industry 4.0 technologies. Companies may provide goods and services to customers more quickly, more affordably, and of higher quality by utilizing supply chain management capabilities, giving them an edge over less-efficient rival.
- Predictive maintenance/analytics—Manufacturers are now able to anticipate possible issues before they exist thanks to Industry 4.0 technologies. Preventive maintenance is performed at your plant depending on schedule or time when IoT systems are not installed. It is, thus, a manual task. Preventive maintenance is significantly more automated and simplified with IoT solutions in place. Systems can alert you to possible difficulties before they grow into larger ones and can detect when gear needs to be repaired. In addition to asking proactive questions like “what is going to happen” and “what can we do to prevent it from occurring,” predictive analytics enables businesses to answer reactionary questions like “what has occurred” and “why did it happen.” Manufacturers may be able to switch from preventive maintenance to predictive maintenance with the use of these analytics.
- Asset tracking and optimization—Industry 4.0 technologies enable manufacturers to use resources more effectively at every level of the supply chain, giving them a greater sense of inventory, quality, and logistical optimization potential. Employees in a factory with IoT can have better global visibility of their assets. Standard asset management processes may be optimized and controlled centrally and in real time for things like asset transfers, disposals, reclassifications, and modifications.
Benefits of Adopting an Industry 4.0 Model
Design, sales, inventories, scheduling, quality, engineering, customer and field service are all included in the scope of Industry 4.0, as well as the complete product life cycle and supply chain. Everyone offers knowledgeable, current, and pertinent perspectives on business and production processes—as well as considerably richer and more timely analytics.

- It makes you more competitive, especially against disruptors like Amazon.
- It makes you more attractive to the younger workforce.
- It makes your team stronger and more collaborative.
- It allows you to address potential issues before they become big problems.
- It allows you to trim costs, boost profits, and fuel growth.
Industry 4.0 is at an inflection point in Indian manufacturing, with more than two-thirds of Indian manufacturers embracing the digital transformation by 2025, thereby contributing to the goal of raising India’s manufacturing GDP to 25%. This research study aims to assess the adoption of Industry 4.0 across India’s manufacturing sector. In-depth inputs from 55 large and mid-sized discrete and process manufacturers and 25 technology providers reveal actionable insights.
Why Should India Adopt Industry 4.0?
As per McKinsey’s analysis, if Indian industries implement key technologies from Industry 4.0 across various sectors like production, logistics, supply chain, and procurement. There are 40% increases in operational cost which is less than 10% of capital cost.
- Advanced data analysis will help its manufacturing capacity and increase the quality of the product. Business Analytics will work on the prediction and prevention of production defects.
- The implementation of automation will reduce manufacturing cycles, decrease cycle time, and will reduce wasteful use of capital.
- Digitization of numerous manufacturing processes will lead to cost reduction with an improved experience for consumers.
- IoT and man-machine connectivity will help supply chains to decrease lead times.
How Is India Preparing for Industry 4.0?
- India has made a lot of efforts to embrace Industry 4.0. According to a research by the Indian Brand Equity Foundation, by 2025, the Indian government wants to increase the manufacturing sector’s contribution to GDP from 16% to 25%. India intends to compete on a global scale with the Make in India program.
- In a nutshell, smart manufacturing is poised to take the place of conventional manufacturing in the globe. Four centers are being developed around the country with cooperation from the Ministry of Heavy Industry and Public Enterprises to help small and medium-sized businesses implement Industry 4.0.
- The Boeing Company provided money for the development of the Centre for Product Design and Manufacturing (CPDM), the country’s first smart factory, at the IISc in Bengaluru. The Internet of Things and data flow during manufacturing assist this smart factory (IoT).
Indian industries that have accepted Industry 4.0
- FMCG: A Cobot is a sort of robot that may be placed close to employees and interact safely with them. India’s FMCG industry has only lately begun utilizing Cobots. Cobots are being used by sectors with worse infrastructure and fewer human resources to speed up operations while consuming less energy.
- Telecommunications Industries: Vodafone Business Services offers intelligent Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity solutions for a range of industries, including transportation, smart cities, healthcare, etc.
- Healthcare Sector: Diabetacare Smart Glucometers are the finest illustration of how patients may use the Internet of Things to monitor blood sugar, blood pressure, and other indicators to manage their diabetes. Industries in India that have embraced Industry 4.0.
To capitalize on evolving technologies, India must deploy Industry 4.0. Industry 4.0 has begun to have an impact in India’s manufacturing and other varied industries. Data-driven decision-making is being used in a variety of industries.
Although some measures have been taken, much more work need to be done. Instead of just spending more money, the emphasis should be on growing the present asset base. Smart manufacturing, data analytics, and the Internet of Things will steer Indian industry in the right way.
Another major barrier to adopting policies is the shortage of qualified labor or the fear of losing employment to automation and other technology. Increasing the number of people with these talents and creating new job categories are two realistic solutions to the problem.
Future: What are the Details of Industry 5.0?
Humans will be able to work more effectively and intelligently thanks to robots and intelligent equipment, and the notion of Industry 5.0 is already being considered. “Industry 5.0 will transform the factory into a place where creative persons can come and work, to create a more tailored and personalized experience for employees and their clients,” said Esben stergaard, chief technology officer and co-founder of Universal Robots.

According to predictions made by Industry 5.0, over 60% of manufacturing, logistics and supply chains, agri-farming, and the mining and oil and gas sectors will hire chief robotics officers by 2025 as a result of the integration of human and machine labor. According to the European Economic Social Committee, “It is certain that robotic automation will spread.
That’s all Folks now Wrapping up!
In today’s competitive business environment, you must utilize solutions that can simplify processes, boost productivity and cooperation, and make real-time use of data. In essence, this should allow for digital transformation. This will enable automated, self-sufficient production with interconnected systems that can collaborate with one another.
The usage of technology will increase productivity by making it easier to track operations and troubleshoot issues. Despite the fact that Industry 4.0 is still in its early stages and that we may not have a whole picture until we look back in 30 years, firms that are utilizing the technology recognize tremendous promise. These same organizations are also grappling with how to acquire new staff with the necessary skills and how to upskill existing employees to take on new job duties enabled by Internet 4.0. Industry 4.0 is a dynamic idea, policy, and vision, with definitions, reference architectures, and standardization all in development. To capitalize on evolving technologies, India must deploy Industry 4.0. Industry 4.0 has begun to have an impact in India’s manufacturing and other varied industries. Data-driven decision-making is being used in a variety of industries.
Although some measures have been taken, much more work need to be done. Instead of just spending more money, the emphasis should be on growing the present asset base. Smart manufacturing, data analytics, and the Internet of Things will steer Indian industry in the right way.
Another major barrier to adopting policies is the shortage of qualified labor or the fear of losing employment to automation and other technology. Increasing the number of people with these talents and creating new job categories are two realistic solutions to the problem.












