Kyoto, Japan- Nuvoton Technology Corporation Japan (NTCJ) has announced the launch of 4th generation of battery monitoring chipset for automotive battery control to measure the voltage and temperature of battery cells and the current of a battery pack with high accuracy.
Achievements:
- Simplifying an automotive battery system; one IC manages up to 25 in-series battery cells
- Battery Management System (BMS) compliant to ASIL-D; redundant measurement system*1 and bidirectional ring communication*2 support its safety
- Offering safety function; a stand-alone chipset which detects abnormalities during car-parking and starts a host microcontroller
- Accurate estimation of battery’s State of Charge (SOC*3) and State of Health (SOH*4); ensured by synchronized current and voltage measurements within 10us.
Product details: https://www.nuvoton.com/products/battery-management/battery-monitoring-ics/automotive-qualified/index.html
With Electric Vehicle (EV) market growth toward a carbon neutral society realization, automobile manufacturers are encouraged to meet demands for a safety improvement of a Lithium-ion battery pack, as well as for a longer EV driving range by enhancing the pack capacity and integration. Furthermore, in order to realize a sustainable society in which mass-produced batteries are reused without being disposed, it is desirable to use batteries for a longer period of time. Not only does BMS secure both high battery capacity and safety, but it also needs a technology that collects various battery parameters such as battery temperature, charging and discharging current to extend battery life.
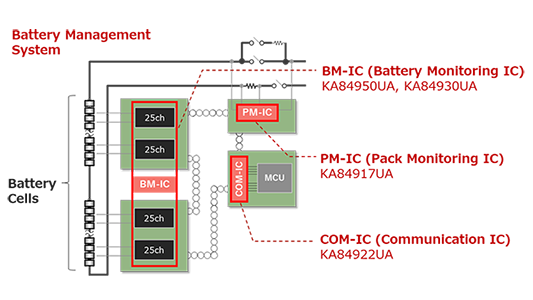
NTCJ launches 4th generation of battery monitoring chipset, consisting of a battery monitoring IC that accurately measures the voltage and temperature of battery cells, a new line of pack monitoring IC that precisely measures a battery pack’s current and monitors its internal control, and a communication IC that serves as an interface with the ICs above and a microcontroller.
Features:
- One IC manages up to 25 battery cells in series, simplifying an automotive battery system that generally consists of 100 to 200 in-series battery cells
NTCJ’s currently developed battery monitoring IC can measure up to 25 in-series battery cells which is a 25 percent increase in number compared to the amount of our conventional products. It contributes to the miniaturization and weight reduction of the battery pack since the BMS with higher-capacity and higher-power can be built with less number of components.
- Redundancy measurement system and daisy-chain communication make it easier to develop and design a BMS in accordance with ASIL-D of ISO26262
For higher safety, NTCJ introduces a redundancy measurement system into the circuits of the battery monitoring IC and the pack monitoring IC to measure the battery parameter.
A daisy-chain communication among chipset ICs adopts bidirectional ring communication to ensure continuous communication in case abnormalities are detected. This redundancy realizes a system with higher robustness, which suppresses communications disruption in case of failures. This makes it easier for car makers and battery pack manufactures to develop and design automotive BMS achieving Automotive Safety Integrity Level D (ASIL-D) of ISO26262.
- Continuous battery monitoring is available in car-parking or microcontroller-in-sleep state to start your system when abnormalities detected
NTCJ’s 4th generation chipset shifts to a low power consumption mode that regularly permits stand-alone monitoring of battery status while the microcontroller is in sleep state. In case abnormalities are detected in the temperature or voltage of the battery cells, the chipset wakes up the microcontroller utilizing the daisy-chain communication to start the BMS.
This function allows to monitor abnormalities of the battery while a car parks or a system sleeps, minimizing system power consumption of batteries. It contributes to a safer system design of EVs which are adaptable to various use scenarios.
- Synchronized current and voltage measurement within 10us improves calculation accuracy of internal impedance in battery cells, resulting in high-accuracy estimation of SOC and SOH
The new chipset automatically synchronizes the voltage of battery cells and the current of the battery pack within 10us to calculate the electric power and internal impedance of the battery with higher accuracy, enabling the BMS to precisely estimate
SOC and SOH of the battery.
Applications:
Battery Electronic Vehicle (BEV), Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV), Energy Storage System (ESS), etc.
Product name:
The 4th generation automotive battery monitoring chipset
Composed of KA84950UA, KA84930UA, KA84917UA, KA84922UA
Specification:
Battery monitoring IC
Typical application:
Mass sales:
Starting from September, 2023
Definitions:
*1. Redundancy measurement system: a system which duplicates all circuits including input terminals of battery cells to ensure the battery parameter continue the measurement in case of failure
*2. Bidirectional ring communication: a communication method which secures alternative communication path in case one path faces abnormalities
*3. State of Charge (SOC): amount of energy available in a battery expressed as a percentage of the battery’s fully charged capacity
*4. State of Health (SOH): an indicator of the degree of battery deterioration; representing Capacity State of Health (SOHC) and Power State of Health (SOHR)












