Microcontrollers are small, powerful devices that act as the brain of numerous modern electronic systems. Despite their diminutive size, these integrated circuits contain a processor, memory, and input/output (I/O) peripherals, making them capable of executing complex instructions and managing various tasks. Microcontrollers are ubiquitous in today’s technology landscape, embedded in everything from household appliances to automotive systems, and industrial machinery to wearable devices. This essay explores the fundamental aspects of microcontrollers, their applications, and their transformative impact on technology.
Anatomy of a Microcontroller
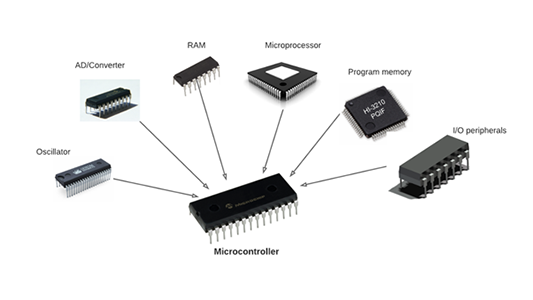
A microcontroller is a type of microprocessor designed specifically for embedded systems. It integrates several key components:
1. Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the core of the microcontroller, executing instructions from the program memory. It can be based on various architectures, such as ARM, AVR, or PIC.
2. Memory: Microcontrollers typically include both volatile memory (RAM) for temporary data storage and non-volatile memory (Flash or EEPROM) for storing the program code and permanent data.
3. I/O Peripherals: These include digital and analog interfaces, timers, counters, and communication modules (e.g., UART, SPI, I2C). These peripherals allow the microcontroller to interact with external devices and sensors.
4. Power Management: Efficient power management is crucial, especially in battery-operated applications. Many microcontrollers have built-in features to manage power consumption, including sleep modes and low-power states.
Applications of Microcontrollers
Microcontrollers are found in a vast array of applications across various industries. Some of the most common applications include:
1. Consumer Electronics: Devices like smartphones, televisions, and home appliances rely heavily on microcontrollers for functionality and user interface management. For instance, a microwave oven uses a microcontroller to control cooking time, power levels, and user inputs.
2. Automotive Systems: Modern vehicles incorporate numerous microcontrollers for engine control, airbag deployment, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and infotainment systems. These microcontrollers enhance vehicle performance, safety, and user experience.
3. Industrial Automation: In manufacturing, microcontrollers are integral to automation and control systems. They manage machinery, process control, and data acquisition, leading to increased efficiency and precision.
4. Medical Devices: Microcontrollers power a range of medical equipment, from simple devices like digital thermometers to complex systems like insulin pumps and MRI machines. They ensure accuracy, reliability, and responsiveness in critical health applications.
5. IoT Devices: The Internet of Things (IoT) revolution relies on microcontrollers to connect and control smart devices. Home automation systems, wearable health monitors, and environmental sensors are just a few examples where microcontrollers play a pivotal role.
The Impact of Microcontrollers on Technology
Microcontrollers have revolutionized technology in several key ways:
1. Miniaturization: The integration of multiple functions into a single chip allows for the development of compact and portable devices. This miniaturization has enabled the creation of wearable technology, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches.
2. Cost Efficiency: Microcontrollers are relatively inexpensive, which lowers the overall cost of electronic products. This affordability has democratized access to advanced technology, making it available to a broader audience.
3. Energy Efficiency: With advanced power management features, microcontrollers contribute to the development of energy-efficient devices. This is particularly important in battery-powered applications, where prolonging battery life is crucial.
4. Customization and Flexibility: Programmable microcontrollers provide developers with the flexibility to customize functionalities according to specific needs. This adaptability is essential in developing specialized applications across different industries.
5. Enhanced Functionality: By integrating various peripherals and interfaces, microcontrollers can handle multiple tasks simultaneously. This capability has led to the development of multifunctional devices, enhancing user convenience and experience.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of microcontrollers promises even greater advancements and innovations. Key trends include:
1. Increased Processing Power: Ongoing developments aim to enhance the processing power of microcontrollers while maintaining low power consumption. This will enable more complex applications and improved performance.
2. Advanced Connectivity: The proliferation of IoT devices requires microcontrollers with robust connectivity options, including advanced wireless protocols like 5G, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), and LoRa.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: Future microcontrollers are expected to incorporate AI and machine learning capabilities, enabling smarter and more autonomous systems. This integration will be pivotal in applications like predictive maintenance and autonomous vehicles.
4. Security Enhancements: As devices become more interconnected, security becomes paramount. Innovations in microcontroller design will focus on enhancing cybersecurity features to protect against threats and vulnerabilities.
5. Eco-Friendly Design: Sustainable development is a growing priority, leading to the design of eco-friendly microcontrollers with lower environmental impact, including the use of biodegradable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing processes.
These insights are based on a report on Microcontrollers Market by Transparency Market Research