Energy management in the automotive industry is becoming increasingly crucial, especially with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs). As cars evolve, so too do the technologies that help manage the energy they consume. This blog will explore energy management in automotive applications, highlighting the role of companies like Mango Semiconductors, which provides essential connectors for these systems.
Energy management refers to the processes and technologies used to monitor, control, and optimize energy consumption. In the automotive context, this involves managing the energy used by the vehicle’s systems, particularly in electric and hybrid vehicles. Effective energy management ensures that vehicles operate efficiently, maximizing range and performance while minimizing waste.
The Role of Energy Management Systems (EMS)
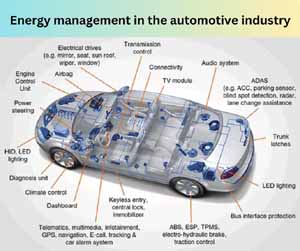
An Energy Management System (EMS) is a comprehensive tool that helps manage energy usage in vehicles. It collects data from various sensors and systems, analyzes this data, and provides insights that can lead to more efficient energy use. For electric vehicles, EMS is vital in managing battery charge levels, optimizing energy distribution to different vehicle components, and ensuring that the vehicle operates within safe temperature ranges.
For example, consider an electric vehicle equipped with an EMS. This system continuously monitors the battery’s charge level, the energy consumption of the motor, and the power used by auxiliary systems like heating and air conditioning. If the EMS detects that the battery is running low, it can adjust the vehicle’s settings to conserve energy, such as reducing power to non-essential systems or adjusting the climate control settings.
The Importance of Thermal Management
One critical aspect of energy management in automotive applications is thermal management. As electric vehicles generate heat during operation, managing this heat is essential to maintain performance and safety. Effective thermal management helps prevent overheating, which can damage components and reduce battery life.
How Thermal Management Works
Thermal management systems use various methods to regulate temperature. These can include:
– Active Cooling: This involves using fans or pumps to circulate coolant around the battery and other components, dissipating heat effectively.
– Passive Cooling: This method relies on materials with high thermal conductivity to naturally dissipate heat without the need for additional energy input.
– Smart Thermal Management: Advanced systems use sensors and data analytics to monitor temperatures in real-time, making adjustments as needed to optimize cooling.
For instance, a smart thermal management system in an electric vehicle might detect that the battery is getting too hot during a long drive. It could automatically activate the cooling system to bring the temperature back down, ensuring the battery operates efficiently and safely.
The Role of Connectors in Energy Management
Mango Semiconductors plays a vital role in the automotive energy management landscape by providing high-quality connectors. These connectors are essential for ensuring reliable connections between various components of the energy management system, including batteries, sensors, and control units.
Why Connectors Matter
Connectors are critical in automotive applications for several reasons:
– Reliability: High-quality connectors ensure that electrical connections remain stable, reducing the risk of failures that could disrupt energy management.
– Efficiency: Efficient connectors minimize energy loss during transmission, helping to maintain the overall efficiency of the vehicle’s energy management system.
– Safety: Properly designed connectors can help prevent overheating and electrical faults, which are crucial for the safety of electric vehicles.
For example, if a connector between the battery and the EMS fails, it could lead to inaccurate readings or even complete system failure. This could result in the vehicle not managing its energy properly, leading to reduced performance or safety risks.
Real-World Example: An Electric Vehicle in Action
Let’s consider a practical example of how energy management and thermal management work together in an electric vehicle. Imagine a family taking a road trip in their electric SUV equipped with an advanced EMS and thermal management system.
As they drive through a hot desert, the EMS continuously monitors the battery’s charge level and the energy consumption of the vehicle’s systems. The thermal management system detects that the battery temperature is rising due to the high ambient temperature and the energy being used to power the air conditioning.
In response, the EMS takes action. It reduces the power supplied to the air conditioning system, ensuring that the battery remains within its optimal operating temperature range. This action helps extend the vehicle’s range, allowing the family to reach their destination without needing to stop for a lengthy recharge. Additionally, the connectors provided by Mango Semiconductors ensure that all systems communicate effectively. If any connector were to fail, the EMS might not receive accurate data about the battery’s condition, leading to poor energy management decisions.