Agentic Al refers to Al systems that can autonomously make decisions and take actions, adapting in real-time and solving multi-step problems with minimal human intervention.
An Al agent for customer service, for instance, could operate beyond simple question-answering. With agentic Al, it could check a user’s outstanding balance and recommend which accounts could pay it off — all while waiting for the user to make a decision so it could complete the transaction accordingly when prompted.
Agentic Al systems ingest vast amounts of data from multiple data sources and third party applications to independently analyze challenges, develop strategies and execute tasks. Businesses are implementing agentic Al to personalize, streamline software development and even facilitate better interactions.
How does Agentic AI work ?
Agentic AI—a term often used interchangeably with Agentic AI—works by enabling artificial intelligence systems to act with autonomy, rather than just react to prompts. These systems are designed as intelligent agents that perceive their environment, make decisions based on goals, plan actions, and execute those actions without continuous human guidance. Unlike traditional AI, which might respond with static answers or generate content, Agentic AI takes initiative: it can gather information, reason through options, adapt to changes, and pursue objectives through multiple steps.
At the core of Agentic
AI is a blend of components such as planning algorithms, memory systems, reinforcement learning, and sometimes multi-modal capabilities (text, code, image). For example, an agent might receive a high-level goal—like “research and summarize the latest trends in climate policy”—and autonomously search sources, filter useful data, compile summaries, and even schedule a presentation. Systems like AutoGPT, BabyAGI, and LangChain-based agents exemplify this by chaining tools, APIs, and reasoning modules to act in real-world environments, opening up vast potential in productivity, automation, and decision-making.
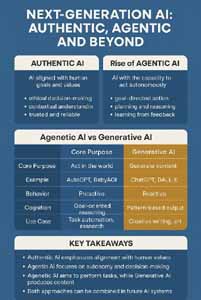
Agentic AI Vs Generative AI Vs Authentic AI
Generative AI, Agentic AI, and Authentic AI each represent different facets of artificial intelligence. Generative AI focuses on creating new content, such as text, images, or music, based on input data and patterns it has learned. Agentic AI refers to systems designed with autonomous decision-making abilities, capable of taking actions to achieve specific goals without human intervention. Authentic AI, often used to describe AI systems with a degree of human-like reasoning, aims to simulate genuine understanding and judgment, prioritizing transparency, ethics, and the alignment of AI behaviors with human values. While generative AI excels in content creation, agentic AI is driven by autonomous task execution, and authentic AI strives to integrate human-like decision-making with ethical considerations.
Rise of Agentic AI
The next leap in artificial intelligence involves giving models agency—the capacity to act independently, make decisions, and carry out tasks in a goal-directed manner. This leads us to the idea of Agentic AI.
Agentic AI systems are designed not just to generate outputs but to plan, reason, and execute. Think of AI agents that don’t just write your emails but read your calendar, analyze priorities, draft responses, and even schedule meetings. These systems combine:
▪Perception (understanding the environment),
▪Cognition (reasoning and decision-making),
▪Action (executing tasks and learning from feedback).
Examples include autonomous research assistants, virtual project managers, and AI-driven robots capable of adapting to dynamic environments.
Agentic AI opens the door to a new era of productivity, where machines aren’t just tools but partners—capable of managing workflows, solving complex problems, and continuously evolving through reinforcement learning and human feedback.
Tools used
Agentic AI relies on a range of tools and frameworks to function effectively, including large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4, orchestration frameworks such as LangChain and Semantic Kernel, and task automation engines like AutoGPT and BabyAGI. These are often integrated with vector databases (e.g., Pinecone, FAISS) for memory and retrieval, APIs and plugins for real-world actions, and planning modules using algorithms like tree search or reinforcement learning. Tools for observation (web scraping, sensors), execution (Python, shell commands), and evaluation (feedback loops, logging) are also crucial for enabling agentic behavior across complex tasks.
Applications
1. Personal virtual assistants
2. Autonomous research agents
3. Automated customer support
4. AI-based project managers
5. Smart healthcare monitoring
6. Financial portfolio management
7. Intelligent tutoring systems
8. Supply chain and logistics automation
9. Legal document analysis and drafting
10. Industrial process control
11. Smart home management
12. Cybersecurity threat detection and response
13. Game testing and adaptive AI characters
14. Personalized marketing automation
15. AI-driven scientific discovery
Limitations
Despite its promise, Agentic AI has significant limitations, including challenges in reliability, safety, and accountability. These systems can make autonomous decisions based on incomplete or biased data, potentially leading to unintended consequences. They also lack genuine understanding or ethical reasoning, which poses risks when used in sensitive domains like healthcare or law. Moreover, debugging and auditing their multi-step behaviors is complex, making transparency and trust difficult to achieve. Their high computational demands and dependency on integration with external tools or APIs further limit their scalability and accessibility for everyday users.
Conclusion
The evolution from generative to agentic and authentic AI marks a profound shift in how we understand intelligence. No longer confined to producing outputs, the AI of tomorrow will be capable of purposeful action, ethical reasoning, and deep collaboration with humans.
In this next-gen AI landscape, we won’t just have smarter tools—we’ll have digital collaborators helping shape a more efficient, thoughtful, and responsive world.
References:
1) “ Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach “(4th ed.) By Russell, S., & Norvig, P.
2) https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/autonomous-agents/
4) Several other web pages are also referred to.